This page has been translated automatically and has not yet been verified by experts.
Hemophilia – редкое наследственное заболевание, связанное с нарушением процесса свёртывания крови. При этом заболевании возникают кровоизлияния в суставы, мышцы и внутренние органы, как спонтанные, так и в результате травмы или хирургического вмешательства.
The coagulation system ensures the preservation of blood inside the vessels, in case of violation of their integrity (injuries, medical interventions), preventing it from pouring outward, closing the damage with special clots (thrombi). Cubbles are formed as a result of biochemical reactions between molecules present in the blood of each person. When studying the coagulation system, they were called "coagulation factors."
Cause повышенной кровоточивости при гемофилии – нарушение синтеза молекул плазменных факторов свертывания. В связи с этим различают следующие основные формы гемофилии:
- hemophilia A – caused by deficiency of the VIII coagulation factor;
- hemophilia b – is due to a deficiency of the IX factor;
Hemophilia A accounts for 80% of cases, hemophilia B – 12%. The remaining 8% are other violations due to the defect in the production of factors or the lack of factors with other numbers.
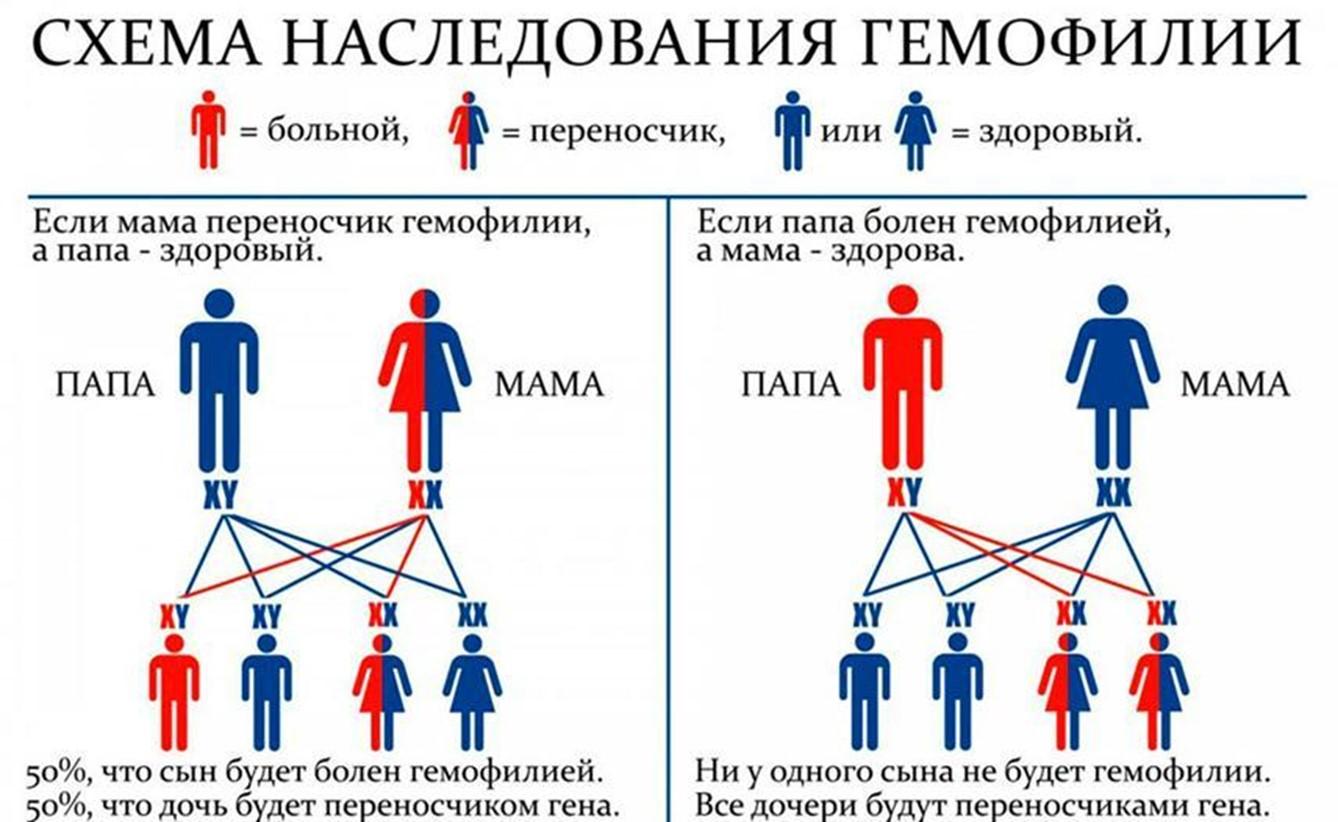
Hemophilia genes are located in the sex x-chromosome, which is transmitted from grandfather to grandson through a healthy daughter-the carrier of the defective gene. That is, men usually suffer from a disease, women act as carriers of hemophilia and can give birth to sick sons or ladder daughters. According to WHO statistics, about one male infant out of 5000 is born with hemophilia A, regardless of national or racial affiliation.
Symptom hemophilii
The leading symptoms of hemophilia A and B are increased bleeding from the first months of life; subcutaneous, intermuscular, subfascial, retroperitoneal hematomas caused by bruises, cuts, various surgical interventions; abundant post -traumatic bleeding; Large joint hemarthrosis, with secondary inflammatory changes.
In newborn children, signs of hemophilia can serve as prolonged bleeding from an umbilical wound, subcutaneous hematomas. Bleeding in children of the first year of life can be associated with teeth teething, sharp edges of the milk teeth can cause biting the tongue, lips, cheeks and bleeding from the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. However, at infants, hemophilia rarely debuts due to the fact that mother's milk contains a sufficient amount of active enzyme – thrombokinase, which can improve the formation of a clot.
The probability of post -traumatic bleeding increases significantly when a child with hemophilia begins to get up and walk. Children after a year are characterized by nasal bleeding, subcutaneous and intermuscular hematomas, and hemorrhages in large joints. Exacerbations of hemorrhagic diathesis occur after infections (SARS, chickenpox, rubella, measles, influenza, etc.) due to violation of vascular permeability. In this case, spontaneous small hemorrhages often occur. Due to constant and prolonged bleeding in children with hemophilia, anemia of varying degrees of severity develops.
A characteristic sign of hemophilia is a delayed nature of bleeding, which usually does not develop immediately after the injury, but after a while, sometimes after 6-12 hours.
Hemophilia is not necessarily inherited. Spontaneous mutations of human DNA are constantly taking place. And therefore, a variant of the occurrence of hemophilia in a family where no one has ever suffered from this disease is possible – the so -called sporadic hemophilia. It is not so rare – in a third of all cases of the disease.
For Diagnostics гемофилии применяется: коагулограмма, определение времени свёртываемости, добавление образцов плазмы с отсутствием одного из факторов свёртывания.
Hemophilia treatment
Replacing therapy is the main method of treating hemophilia. For this purpose, concentrates of the VIII and IX factors of blood coagulation in individual doses for each patient and the type of bleeding are used.
Prevention Hemophilia
In order to prevent the birth of a child with hemophilia, medical and genetic counseling is carried out, prenatal diagnosis is possible.